ProstateNext®
Since hereditary prostate cancer is not well understood or often recognized, clinicians need clear results to guide treatment decisions. ProstateNext is a 14-gene panel which offers more precision to identify and manage hereditary prostate cancer.
| Test Code | 8845 |
| Turnaround Time (TAT) | 14-21 days |
| Number of Genes | 14 |
Ordering Options
- AmbryPort Login or Create an Account
- Order a Sample Kit
We offer family variant testing at no additional cost
We offer family variant testing for all blood relatives of patients who undergo full single gene sequencing, multigene panel testing or exome sequencing at Ambry Genetics and are found to have a pathogenic or likely pathogenic variant. Testing must be completed within 90 days of the original report date. Whenever possible, more closely related relatives should be tested before more distant relatives. If you or a family member are interested in learning more about our family testing program or when family testing may be clinically indicated, please contact us or your provider for additional information. Note that Ambry can only provide such family testing services to patients receiving medical care in the U.S or US territories.
Order NowWhy Is This Important?
- Option to modify frequency and initial age of prostate cancer screening
- Consideration of risk-reducing measures for your patient and/or their family members
- Option to tailor treatments (e.g. PARP inhibitors for prostate cancer patients who have ATM or BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations)
- Identify at-risk family members
When To Consider Testing
- Early-onset prostate cancer (diagnosed <50 years of age)
- Metastatic prostate cancer at any age
- Multiple primary cancers in one person (e.g. prostate and male breast cancer)
- Personal history of prostate cancer and >1 family members* with breast cancer (<50 years of age) and/or invasive ovarian cancer
- Personal history of prostate cancer and >2 family members* with breast, pancreatic, or prostate cancer
* On the same side of the family
Mutation Distribution and Detection Rates*
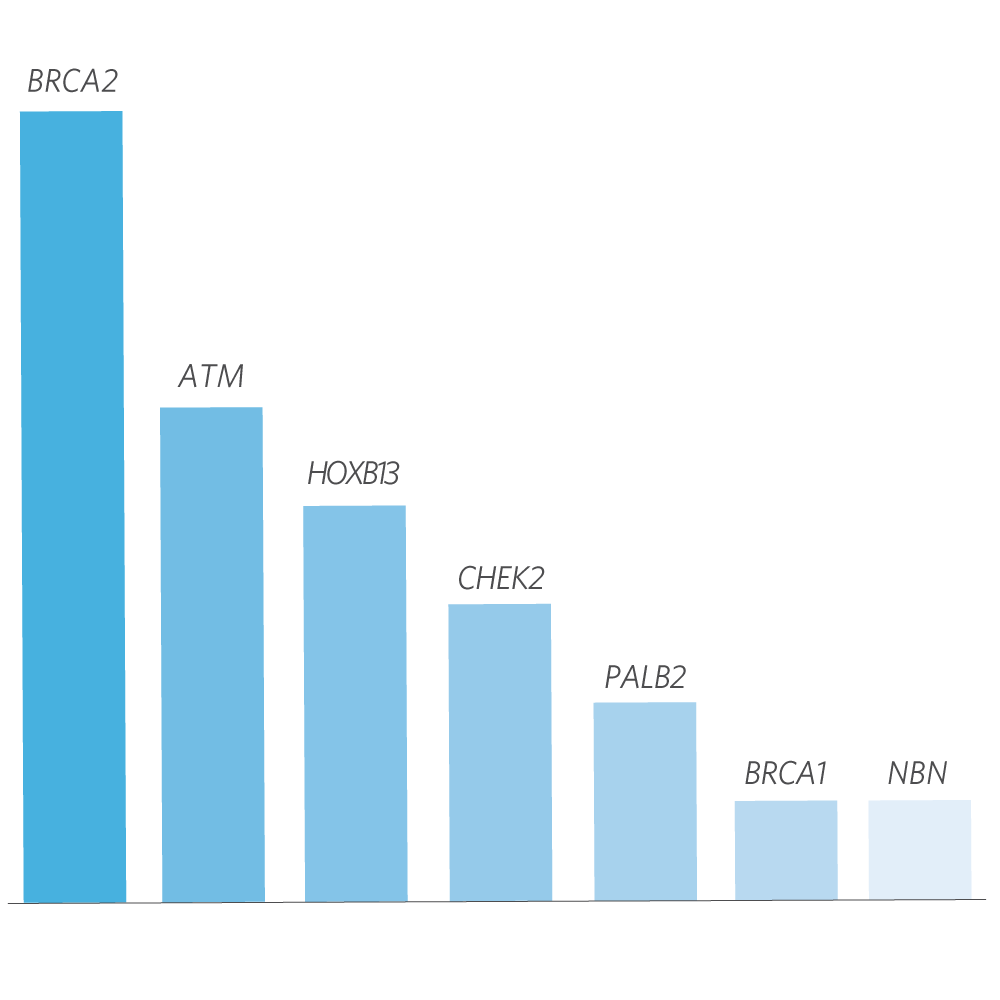
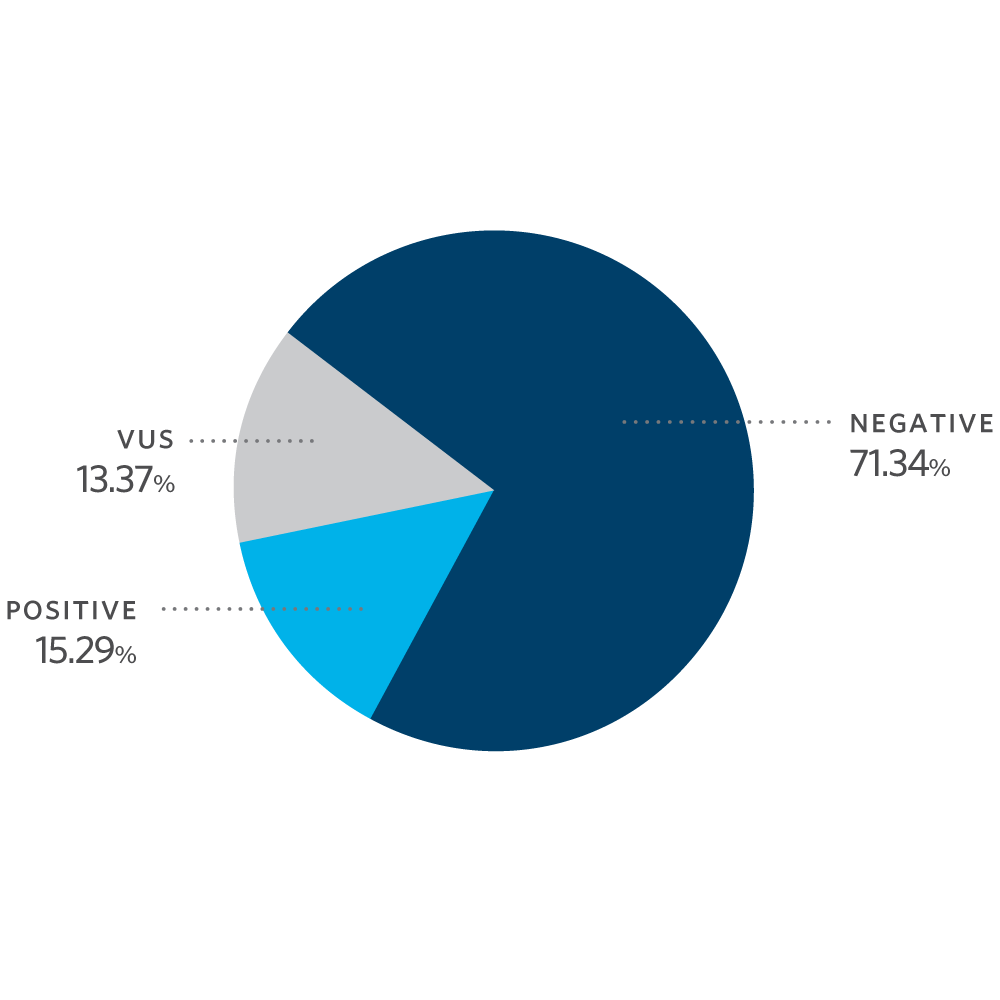
* Excludes MUTYH carriers, APC p.l1307K, and CHEK2 p.l157T
Test Description
ProstateNext analyzes 14 genes (listed above). These genes (excluding EPCAM) are evaluated by next generation sequencing (NGS) or Sanger sequencing of all coding domains, and well into the flanking 5’ and 3’ ends of all the introns and untranslated regions. For HOXB13, only variants impacting codon 84 are routinely reported. The inversion of coding exons 1-7 of the MSH2 gene and the BRCA2 Portuguese founder mutation, c.156_157insAlu (also known as 384insAlu) are detected by NGS and confirmed by MLPA. Clinically significant intronic findings beyond 5 base pairs are always reported. Intronic variants of unknown or unlikely clinical significance are not reported beyond 5 base pairs from the splice junction. Additional Sanger sequencing is performed for any regions missing or with insufficient read depth coverage for reliable heterozygous variant detection. Potentially homozygous variants, variants in regions complicated by pseudogene interference, and variant calls not satisfying depth of coverage and variant allele frequency quality thresholds are verified by Sanger sequencing. Gross deletion/duplication analysis is performed for the covered exons and untranslated regions of all sequenced genes (excluding HOXB13 and PMS2) using read-depth from NGS data with confirmatory multiplex ligation-dependent probe amplification (MLPA) and/or targeted chromosomal microarray. For EPCAM, only gross deletions encompassing the 3’ end of the gene are reported. For PMS2, gross deletion/duplication analysis is performed using MLPA. If a deletion is detected in exons 13, 14, or 15 of PMS2, double stranded sequencing of the appropriate exon(s) of the pseudogene, PMS2CL, will be performed to determine if the deletion is located in the PMS2 gene or pseudogene.